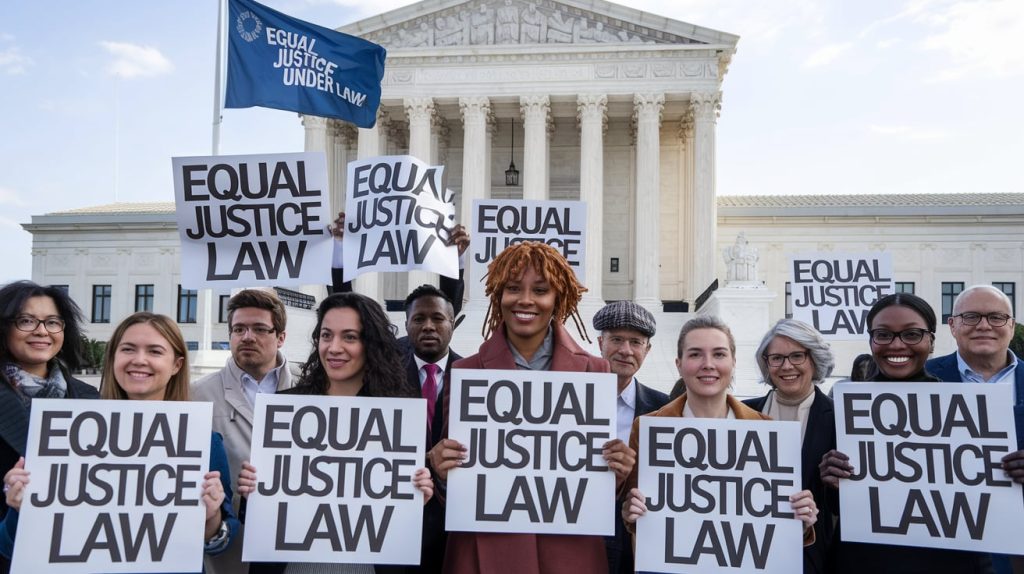
The 14th Amendment to the United States Constitution, adopted on July 9, 1868, is one of the most pivotal amendments in American history. It profoundly shaped civil rights and continues to influence legal and political discourse. This article explores the rights protected under the 14th Amendment, focusing on its clauses, historical significance, and its impact on contemporary legal cases.
Key Clauses of the 14th Amendment
The 14th Amendment comprises five sections, but its core principles are found in the first section, which includes three vital clauses:
1. Citizenship Clause
- Purpose: Establishes who qualifies as a U.S. citizen.
- Text: “All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside.”
- Impact: It grants citizenship to all individuals born or naturalized in the U.S., including formerly enslaved individuals, thereby overruling the Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857) decision.
2. Due Process Clause
- Purpose: Protects individuals from being deprived of life, liberty, or property without due process of law.
- Text: “No State shall… deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law.”
- Impact: This clause ensures fair treatment under the law and has been interpreted to protect fundamental rights such as privacy, marriage, and bodily autonomy.
3. Equal Protection Clause
- Purpose: Prohibits states from denying any person within their jurisdiction equal protection of the laws.
- Text: “No State shall… deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.”
- Impact: This clause serves as the foundation for many landmark civil rights cases, addressing issues such as racial segregation, gender discrimination, and LGBTQ+ rights.
Historical Significance
The 14th Amendment emerged during the Reconstruction Era after the Civil War, primarily to address the injustices faced by newly freed African Americans. Its passage marked a significant step toward a more inclusive definition of citizenship and equality. However, its interpretation and application have evolved over time.
Landmark Cases Involving the 14th Amendment
1. Brown v. Board of Education (1954)
- Issue: Racial segregation in public schools.
- Outcome: The Supreme Court ruled that segregation violated the Equal Protection Clause, declaring “separate but equal” unconstitutional.
2. Roe v. Wade (1973)
- Issue: Abortion rights.
- Outcome: The Court relied on the Due Process Clause to protect a woman’s right to privacy in making medical decisions.
3. Obergefell v. Hodges (2015)
- Issue: Same-sex marriage.
- Outcome: The Court ruled that bans on same-sex marriage violated the Equal Protection and Due Process Clauses, legalizing same-sex marriage nationwide.
Modern-Day Implications
The 14th Amendment remains a cornerstone of legal arguments in the United States. Whether addressing police misconduct, voting rights, or discrimination, its principles are invoked to uphold justice and equality. Legal scholars often refer to it as a “living amendment” because its interpretation adapts to societal changes.
The 14th Amendment underscores the fundamental values of democracy, ensuring that no person is denied the rights and liberties guaranteed by the Constitution. As society evolves, the 14th Amendment remains a beacon of hope for achieving true equality in the United States.
References:
- U.S. National Archives. “The 14th Amendment to the United States Constitution.”
- Supreme Court Cases and Analysis on the 14th Amendment.